

Origin Protocol (OGN) x Cyberscope Audit - Case Study

The OGN Ecosystem
Origin Protocol is a web3 protocol aiming to bring non-fungible tokens (NFTs) and decentralized finance (DeFi) to the masses.
The OGN team has a huge experience in building blockchain products. Origin Protocol is a decentralized platform that aims to enable the creation of peer-to-peer (P2P) marketplaces. The platform is built on the Ethereum blockchain and utilizes smart contracts to facilitate transactions and the creation of decentralized applications (dApps). The native token of the platform is called OGN (Origin Protocol token), which is used to incentivize participation in the network and to pay for various services within the Origin ecosystem. OGN can also be used to vote on governance decisions and access certain features on the platform.
OGN token market cap valuation is more than 50 million, covering more than 5 million in trading volume per day. It is exchanged in more than 70 exchanges including Binance, Coinbase, KuCoin, and Kraken.
Numbers and Challenges
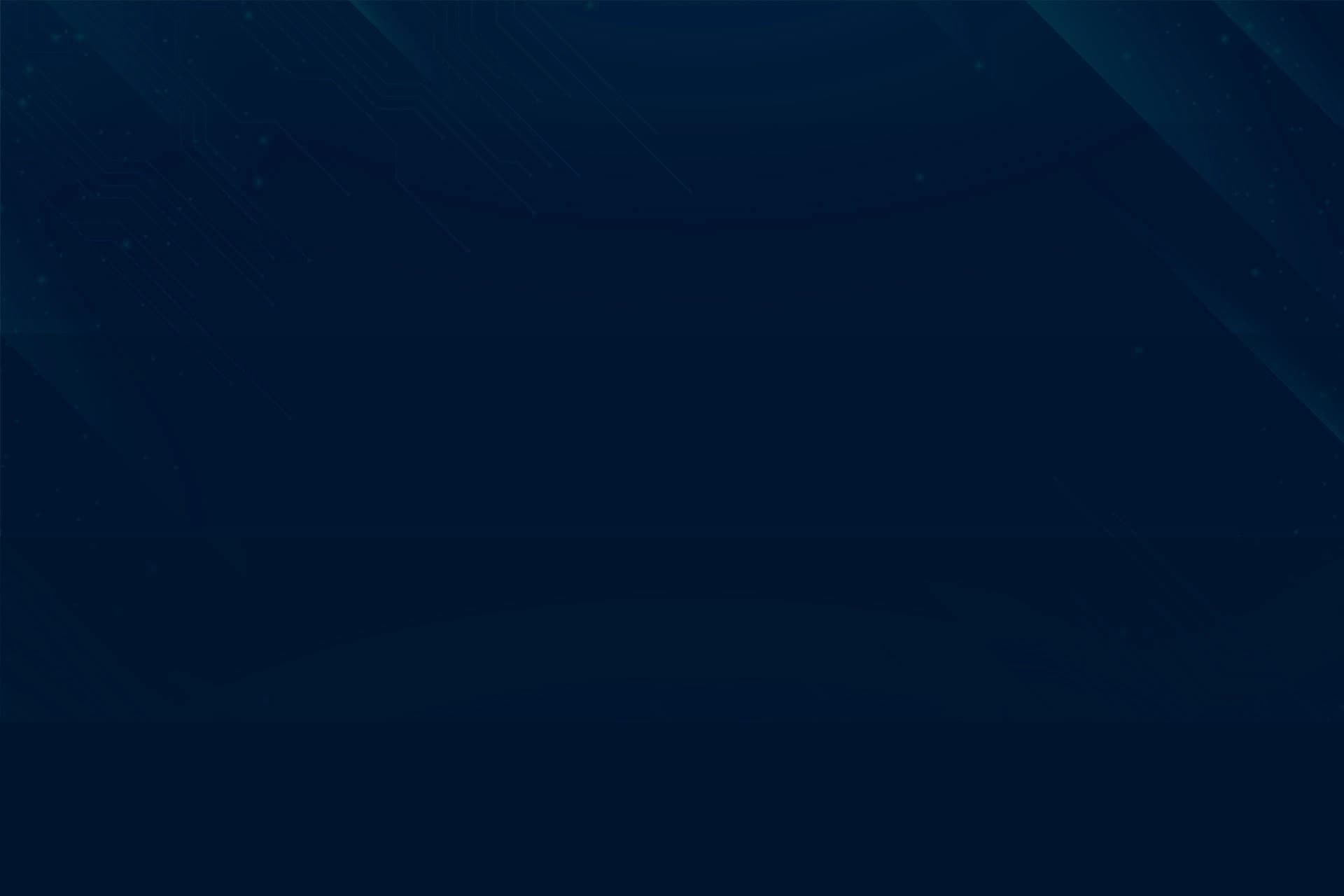
OGN security is an essential and integral part of the ecosystem. They have introduced dozens of decentralized applications and features. Hundreds of different developers have implemented these applications over a long time period. The following numbers are some of the statistics from the official Origin Protocol repository.
- 3,121 commits
- 750 Pull requests
- 500 thousand lines of code
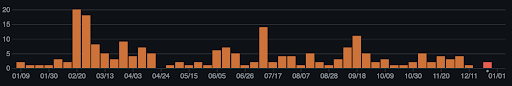
The OGN products are used by thousands of users in the decentralized world. The OGN popularity combined with the code base diversity poses a challenging cybersecurity task.
Cyberscope audit experts were chosen in order to tackle this challenging task. In the initial collaboration between OGN and Cyberscope, the staking contract was selected to be audited.
An audit of a staking contract is important because it can help to ensure that the contract is functioning as intended and that it is secure and reliable. A staking smart contract audit can help identify any contract issues, such as bugs or vulnerabilities, and provide recommendations on how to fix those issues. This can help to promote confidence and trust in the staking process and the overall security of the ecosystem.
You can find OGN’s staking contract in the official repository.
Staking Contract Audit
One of the main responsibilities of Cyberscope’s auditors was to ensure that the staking is reliable, secure, and functioning as intended.
Getting a smart contract audit for any staking contract is a crucial part of every project. An independent and objective assessment of a smart contract, by a reputable third-party cybersecurity firm like Cyberscope, can give the investors of the project confidence and assurance that the staking will work as intended.
Immediately after getting in touch with OGN’s team, Cyberscope’s auditors got to work. Initially, the audit process was split into separate steps. Each step was an essential part of the final audit report.
Step 1. Reviewing the code
OGN’s staking contract was assigned to two senior solidity auditors to review the code of the smart contract and to ensure that it is well-written, follows best practices, and is free of errors and vulnerabilities. Since this is one of the most critical parts of the audit, Cyberscope is always using two auditors to make sure that they will peer review each other’s work and cover as many issues as possible.
Step 2. Testing the contract
The auditors run numerous tests on the smart contract to ensure that it is functioning as intended and that it can handle all possible scenarios correctly. The contract was deployed in a local environment so it can be called by the auditors.
Step 3. Evaluating the contract's security
The auditors assessed the security of the smart contract to ensure that it is resistant to attacks and that it has appropriate safeguards in place to protect against unauthorized access.
Step 4. Providing Recommendations
When the auditors identified issues with the smart contract, they provided recommendations for how to address those issues and make the contract more reliable and secure.
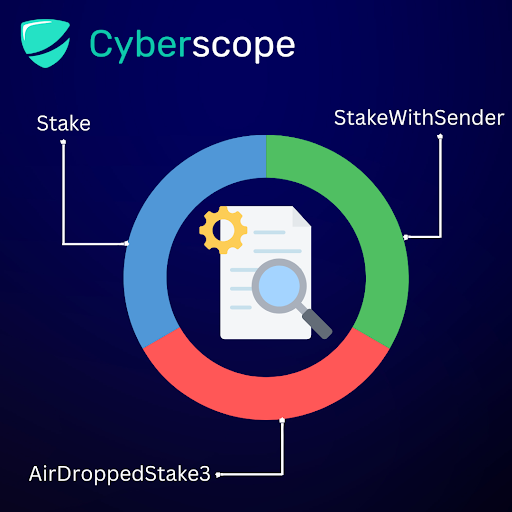
Staking Contract Features Breakdown
The cyberscope team investigated thoroughly the basic functionality that the staking contract provides.
- Stake, any user has the ability to stake any amount of tokens for a specific duration and rate.
- StakeWithSender, the contract of the staking token has the ability to stake any amount of tokens for a specific duration and rate.
- AirDroppedStake, some users that are picked by the staking contract admins have the ability to stake tokens for a predefined amount, duration, and rate.
The audit assessment report mentions all the logical entities, the permissions that are required for each entity, and their dependencies.
Each feature was checked in combination with the rates and duration that the business logic of the staking contract provides. One of the most tricky parts of a staking contract is the balance. The contract’s balance is a combination of different variations:
- The healthy state of Annual Percentage Yield (APY) and Annual Percentage Rate (APR).
- The contract reserves.
- The emergency withdraws.
- The rewards claim functionality in edge cases like the beginning and the end of the staking period.
Main Assessment
In the main assessment delivery, the Cyberscope team reported 9 findings varying between potential overflows, transfer amount inconsistency, and performance optimizations. The audit also commented on the business logic approaches, the issues that may be produced, and the possible recommendations that could be applied. For instance, the Merkle proof mechanism was picked as one of the alternatives in order to add the airdrop winners in the smart contract efficiently.
OGN is an open-source repository with many contributors and the audit findings require some time to be processed and resolved. Some of the findings were added by the contributors in the public repository tickets so they can also be handled by the community.
Some of the issues: https://github.com/OriginProtocol/origin-dollar/issues/1194
Never-Ending Roadmap
OGN has an ever-evolving roadmap with many new features and decentralized applications under development. The more code is added, the more maintenance and security are required. When the code base is increased linearly to an enormous code base like OGN, then the complexity and the vulnerabilities are increased exponentially.
The Cyberscope team has committed to helping the OGN ecosystem to keep growing. It is not a waterfall security assessment, but a never-ending circle. The success of the OGN project is also a success for the Cyberscope team. That’s the reason that the OGN foundation chose to work with one of the experts in the cybersecurity industry.
Read the full report here.


